Fix Inventory Notebook
Fix Inventory Notebook is a library that allows you to interact with Fix Inventory Core using Jupyter Notebook, a web-based interactive Python shell. It is a powerful tool for interactive data analysis and visualization.
Installation
Simply install the fixnotebook package and Jupyter's notebook package using pip:
pip install notebook fixnotebook
Then, start Jupyter Notebook:
jupyter notebook
Usage
Setup
First, create a new notebook by clicking New → Python 3:
Then, instantiate the FixNotebook object with the URL and PSK (if configured) of your Fix Inventory Core instance:
from fixnotebook import FixNotebook
rnb = FixNotebook("https://localhost:8900", psk=None)
Visualization
Visualizing the dependencies between resources as a graph can be useful to understand what's running in your cloud. Here are some examples:
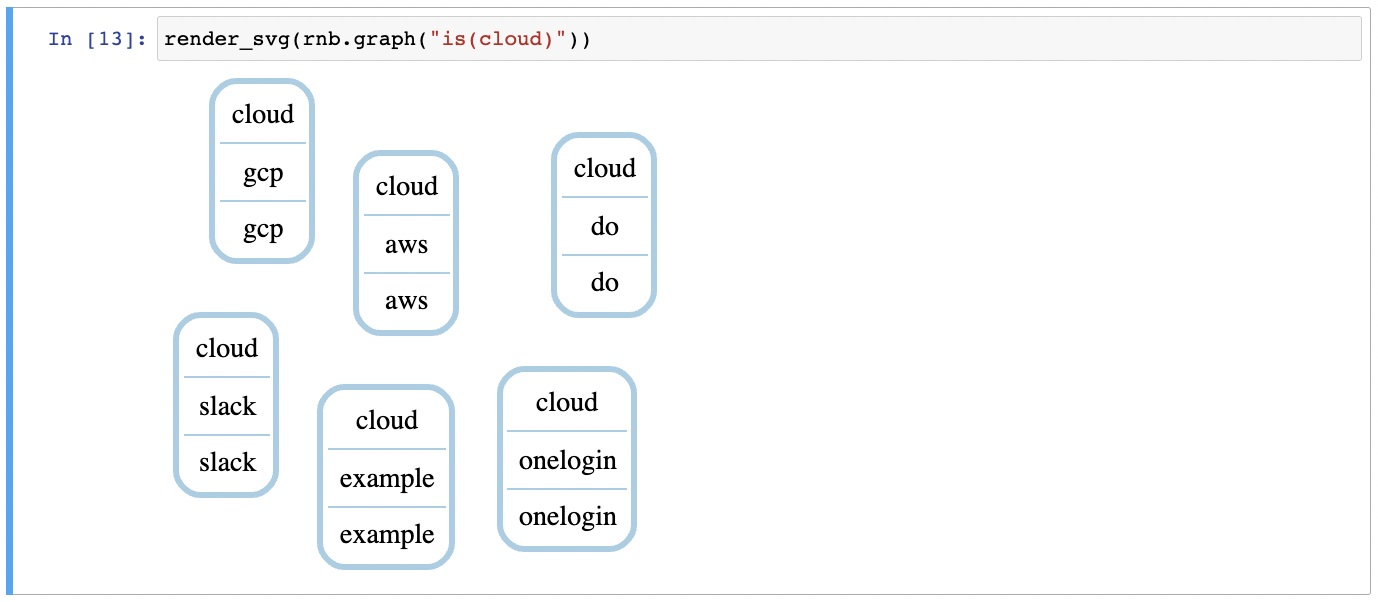
Render the accounts as an svg graph:
from IPython.display import display_png as render_png, display_svg as render_svg
render_svg(rnb.graph("is(cloud)"))
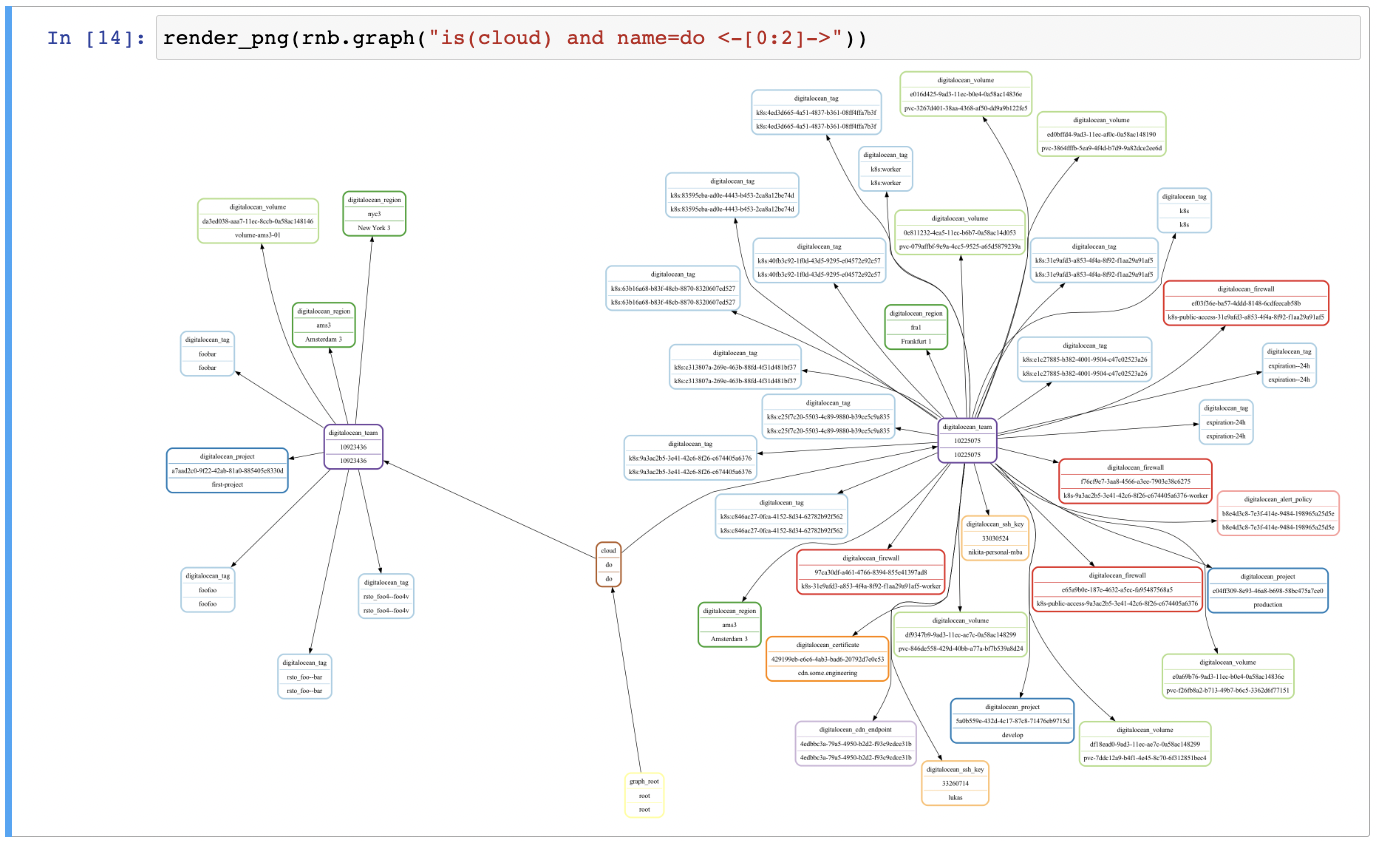
Make a graph of all clouds with name do and their successors one level deep and render it as a PNG image:
render_png(rnb.graph("is(cloud) and name=do <-[0:2]->"))
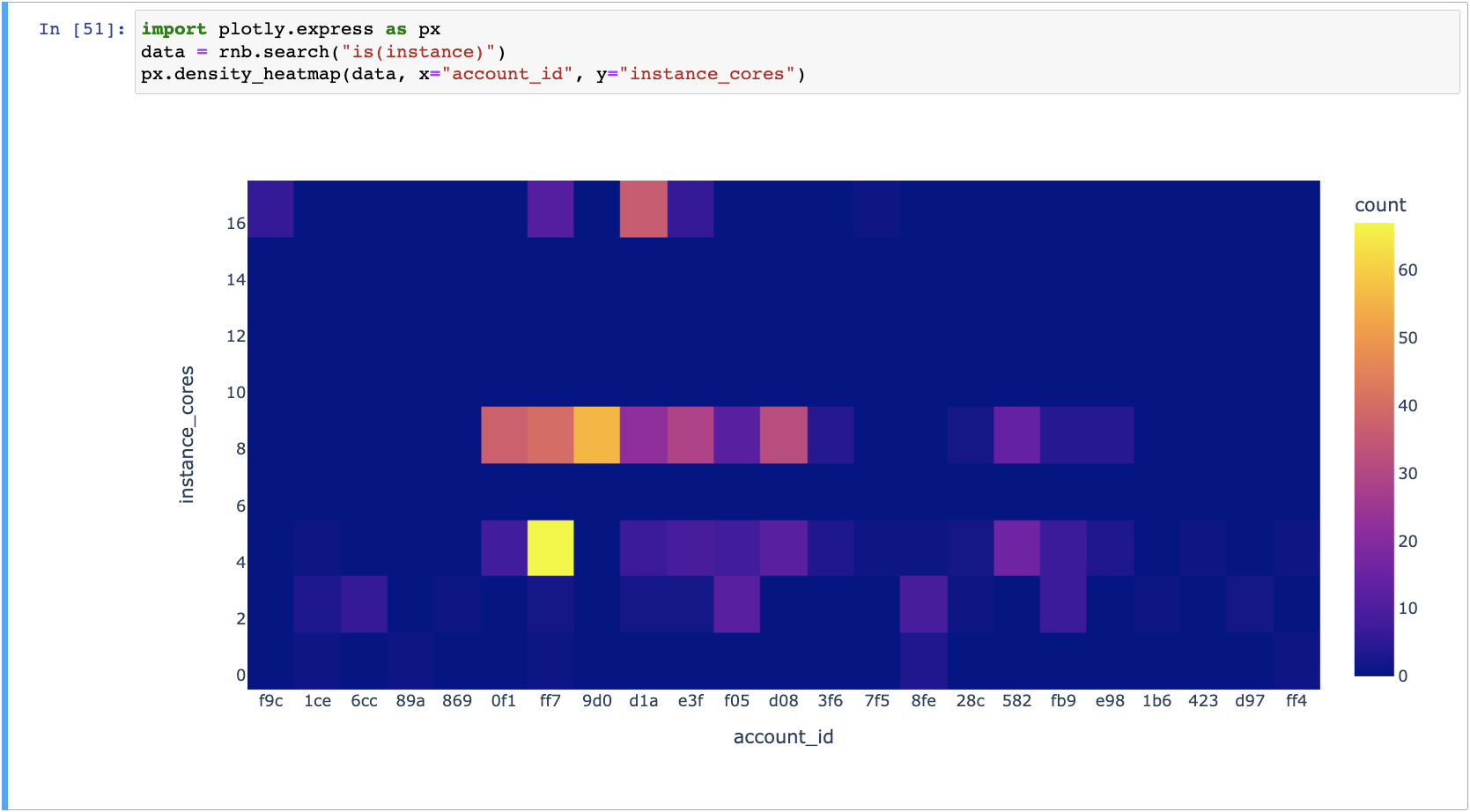
Show the instances/cores/account heatmap, to see which accounts use a lot of expensive instances:
import plotly.express as px
data = rnb.search("is(instance)")
px.density_heatmap(data, x="account_id", y="instance_cores")
Full-Text Search
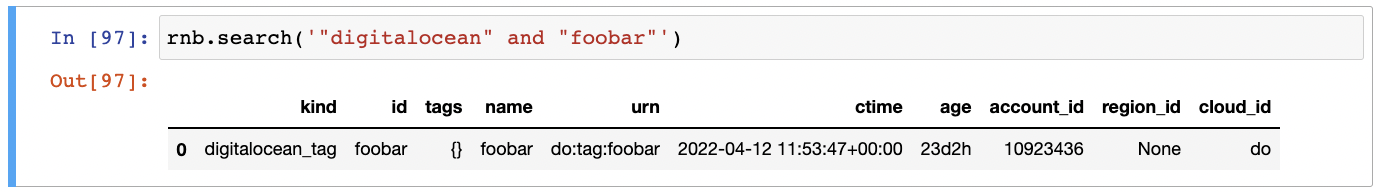
Search all resources for a properties with values digitalocean and foobar. Full text search is useful when you have a keyword, e.g. e-mail address or name, and you want to find all resources related to it:
rnb.search('"digitalocean" and "foobar"')
Counting
Get number of all collected instances by kind:
rnb.search("is(instance)").groupby(["kind"])["kind"].count()

Searching by Kind
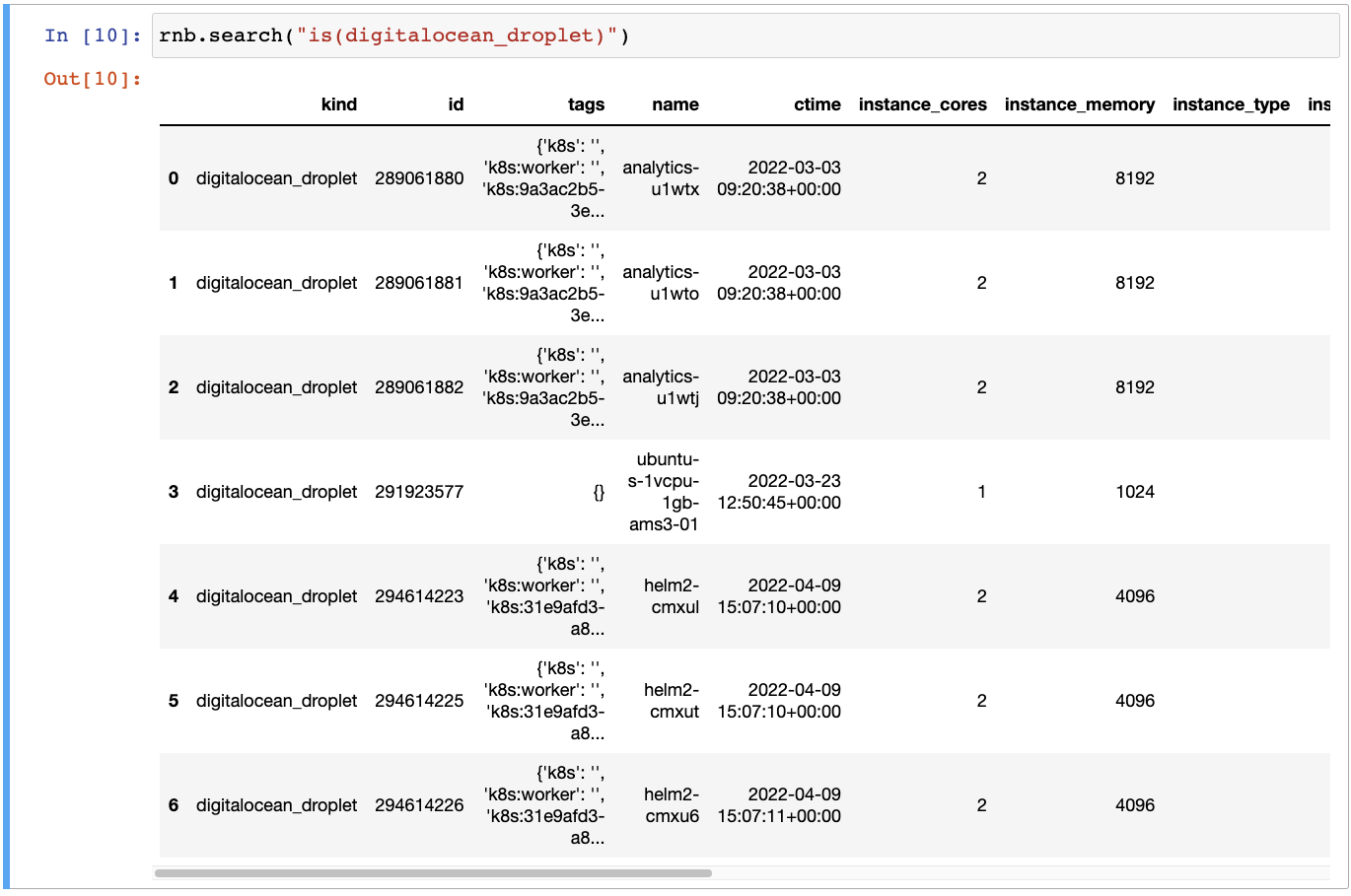
Get list of all the DigitalOcean droplets:
rnb.search("is(digitalocean_droplet)")
Selecting Properties
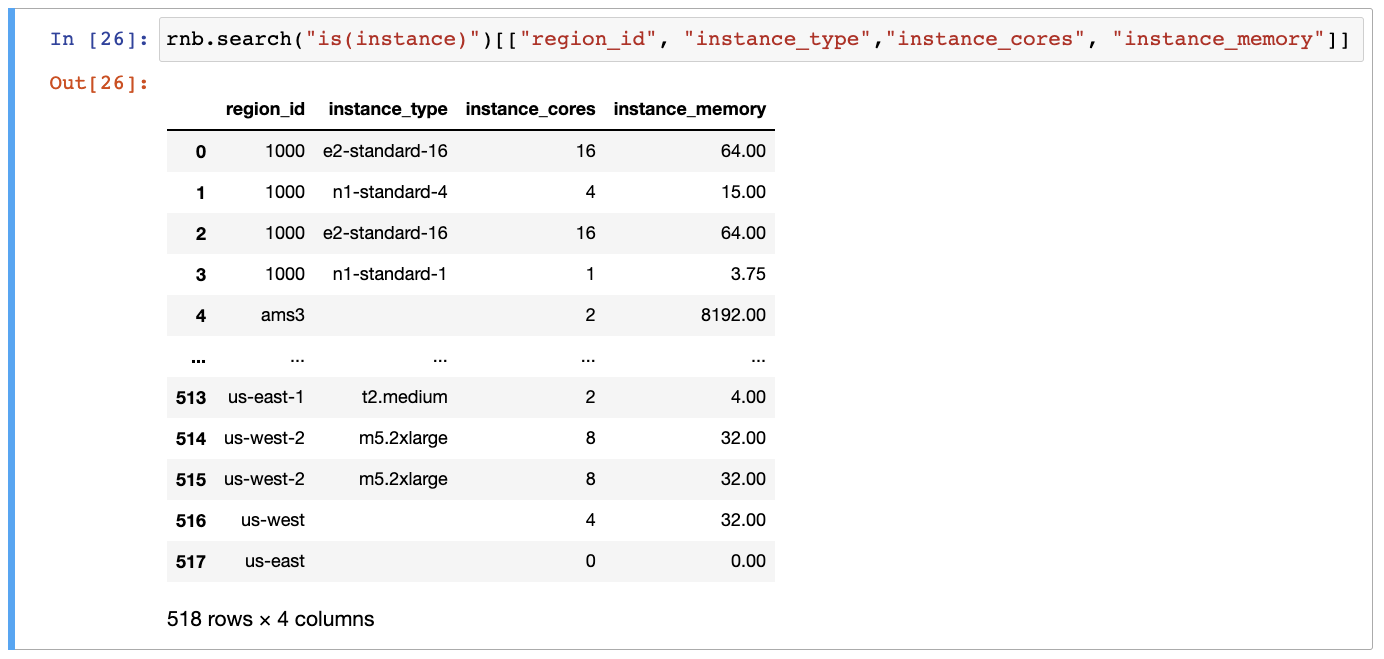
Get list of name, type, cores, and memory for each instance:
rnb.search("is(instance)")[["region_id", "instance_type","instance_cores", "instance_memory"]]
Filtering
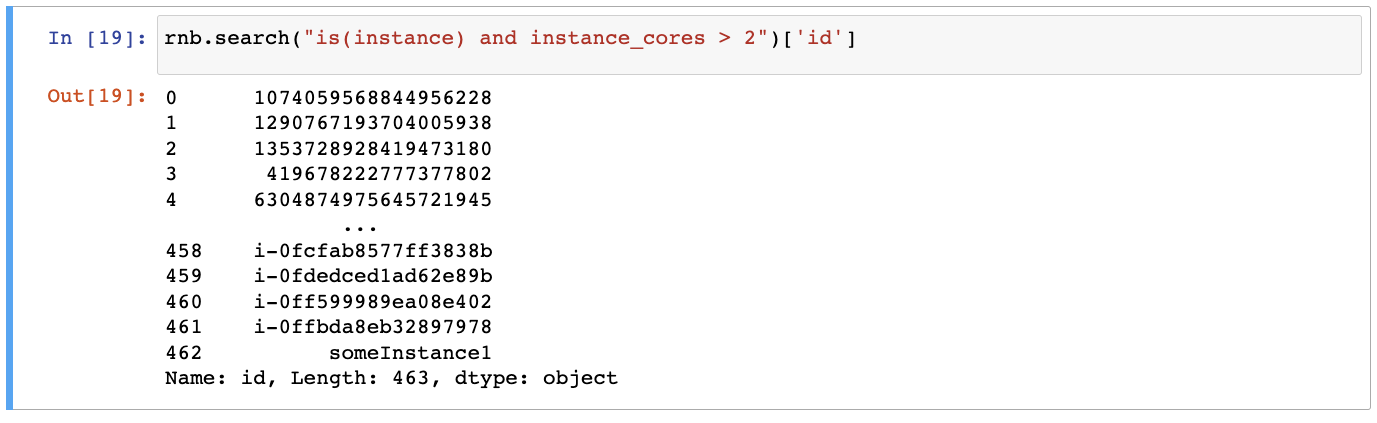
Get list of all compute instances with more than two CPU cores:
rnb.search("is(instance) and instance_cores > 2")['id']
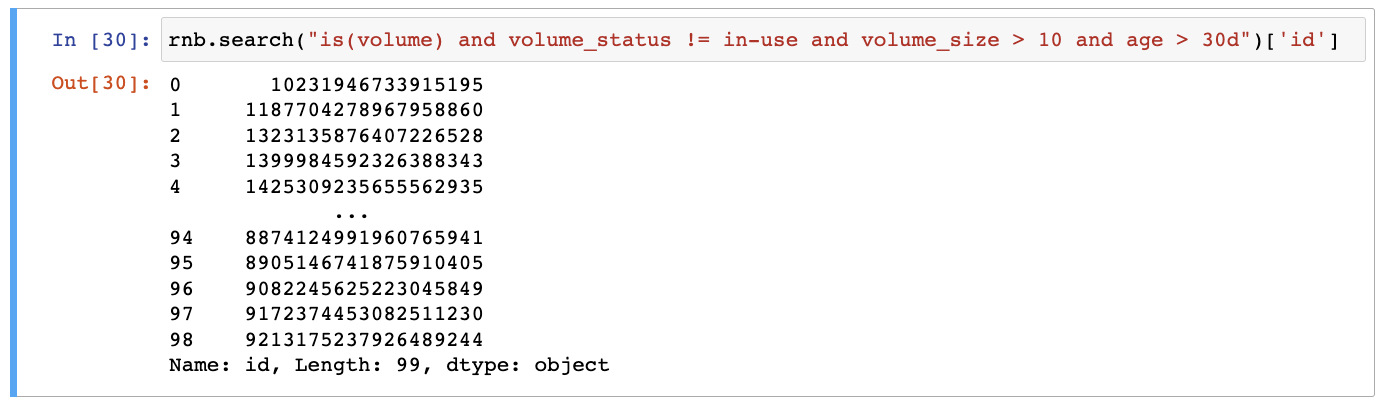
Get list volumes that are not in use, larger than 10GB, older than 30 days.
rnb.search("is(volume) and volume_status != in-use and volume_size > 10 and age > 30d")['id']
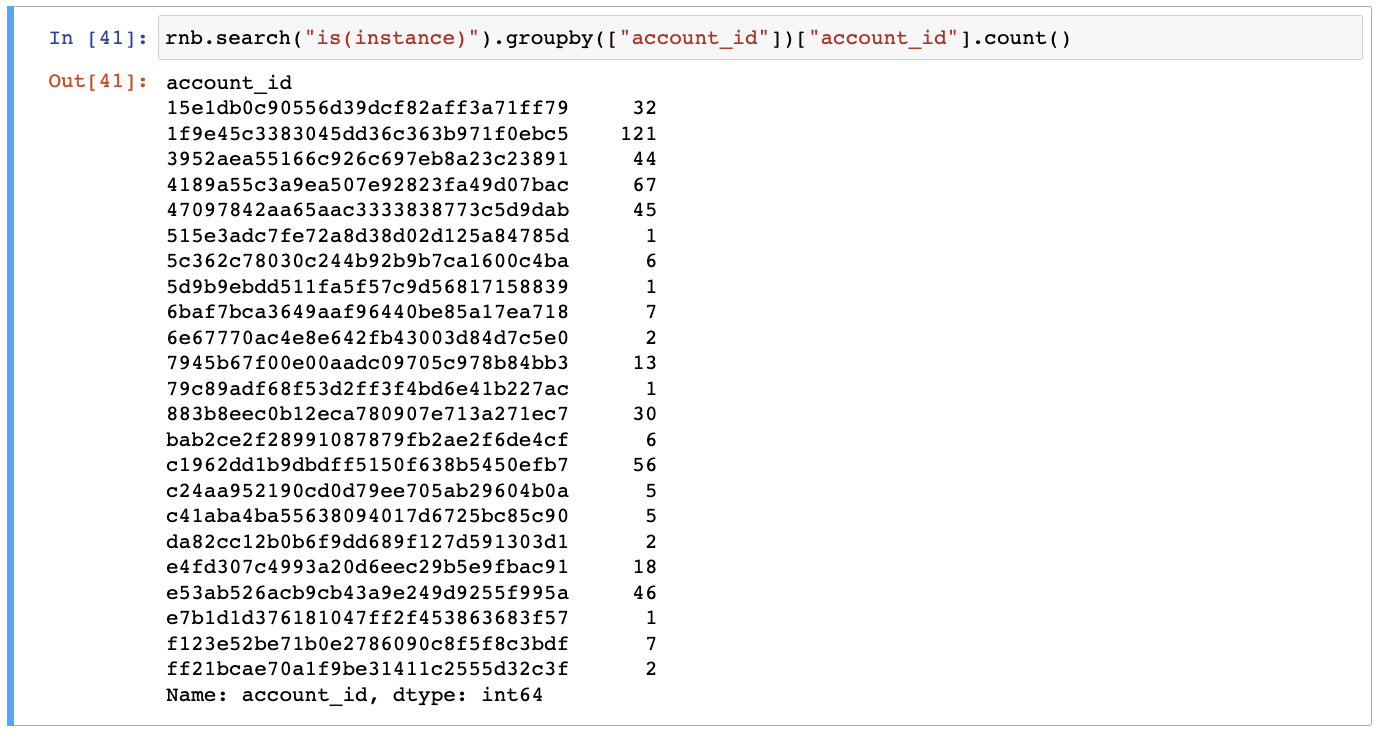
Aggregation
Count the number of instances by account ID:
rnb.search("is(instance)").groupby(["account_id"])["account_id"].count()
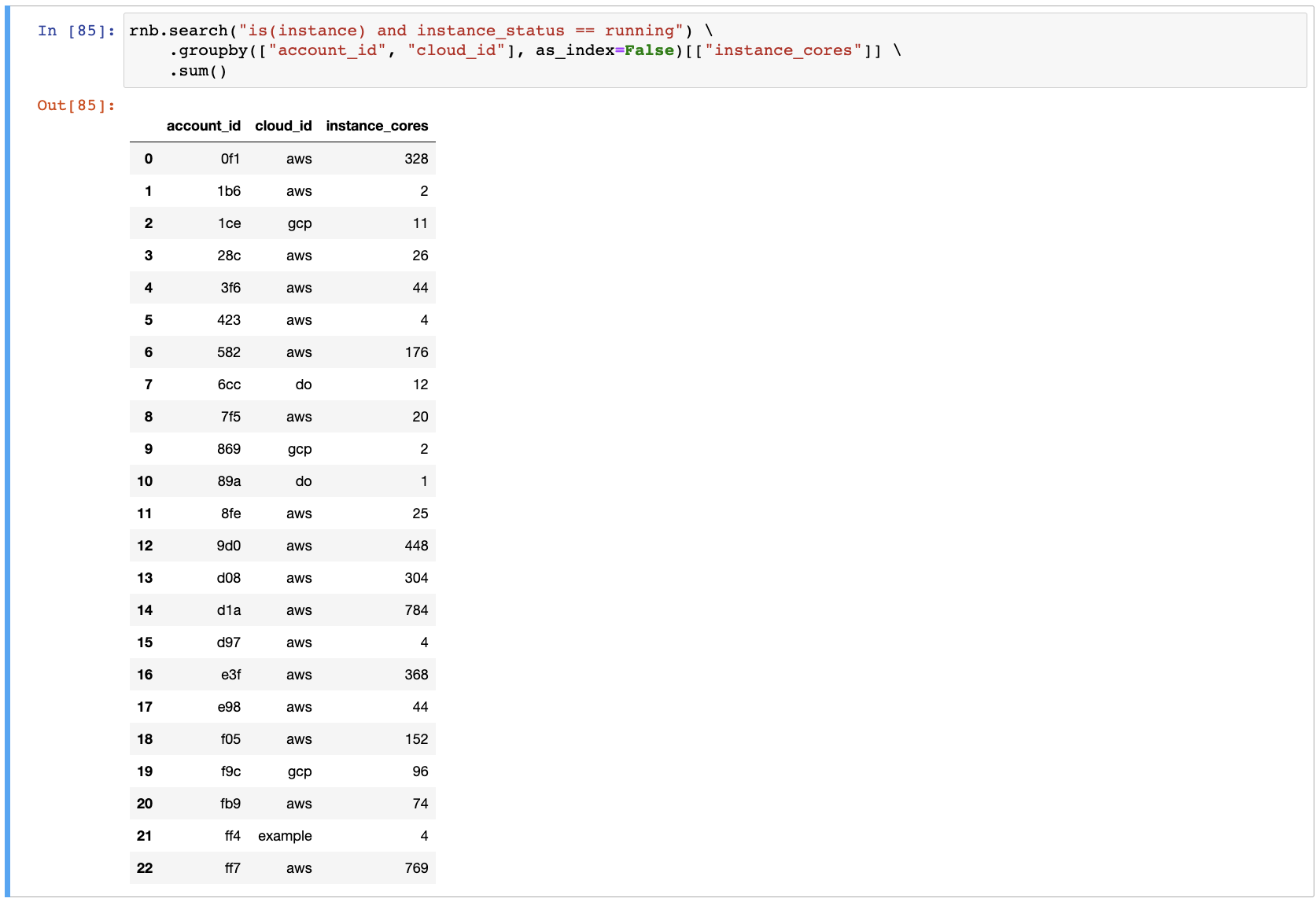
Aggregate CPU cores data grouped by account and cloud. This is useful for identifying the most expensive accounts:
rnb.search("is(instance) and instance_status == running") \
.groupby(["account_id", "cloud_id"], as_index=False)[["instance_cores"]] \
.sum()
Next Steps
You can find the examples from this page in the someengineering/fixinventorynotebook GitHub repository.
That's it for now. Happy exploring!